Khan Academy Video Tutorial. Introduction to basic algebraic equations of the form Ax=B
- Subject:
- Algebra
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Teaching/Learning Strategy
- Date Added:
- 08/05/2020

Khan Academy Video Tutorial. Introduction to basic algebraic equations of the form Ax=B

This is a short unit introducing expressions.
Algebra students need practice determining equations of lines given a pair of points, or the line parallel or perpendicular to a given line through a given point. This Demonstration, along with guiding worksheets or a teacher presentation, gives students a chance to see the relationships between these lines and points.
This web-based graphing activity explores the similarities and differences between Velocity vs. Time and Position vs. Time graphs. It interactively accepts user inputs in creating "prediction graphs", then provides real-time animations of the process being analyzed. Learners will annotate graphs to explain changes in motion, respond to question sets, and analyze why the two types of graphs appear as they do. It is appropriate for secondary physical science courses, and may also be used for remediation in preparatory high school physics courses. This item is part of the Concord Consortium, a nonprofit research and development organization dedicated to transforming education through technology. Users must register to access full functionality of all the tools available with SmartGraphs.

The typical system of equations or inequalities problem gives the system and asks for the graph of the solution. This task turns the problem around. It gives a solution set and asks for the system that corresponds to it. The purpose of this task is to give students a chance to go beyond the typical problem and make the connections between points in the coordinate plane and solutions to inequalities and equations. Students have to focus on what the graph is showing.
Students have mastered solving equations and looking at solutions graphically. This unit is an extension and will have students investigate how to find to two equations. This unit will utilize investigate and exploration, with some direct instruction, to solidify the process and procedures to finding and identifying solutions to systems.
Students will be able to solve a system of equations using substitution, elimination and graphing techniques. Primary focus is on linear systems with two variables. Exploration is on systems involving quadratics, linears and circles with graphing.

This lesson examines the process of completing the square as a method of solving quadratic equations.

Introduction to a selection of mathematical topics that are not covered in traditional mechanical engineering curricula, such as differential geometry, integral geometry, discrete computational geometry, graph theory and optimization techniques. Emphasis on basic ideas and on applications in mechanical engineering. Selection will change every year. This course forms an introduction to a selection of mathematical topics that are not covered in traditional mechanical engineering curricula, such as differential geometry, integral geometry, discrete computational geometry, graph theory, optimization techniques, calculus of variations and linear algebra. The topics covered in any particular year depend on the interest of the students and instructor. Emphasis is on basic ideas and on applications in mechanical engineering. This year, the subject focuses on selected topics from linear algebra and the calculus of variations. It is aimed mainly (but not exclusively) at students aiming to study mechanics (solid mechanics, fluid mechanics, energy methods etc.), and the course introduces some of the mathematical tools used in these subjects. Applications are related primarily (but not exclusively) to the microstructures of crystalline solids.
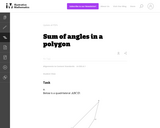
This problem provides students with an opportunity to discover algebraic structure in a geometric context. More specifically, the student will need to divide up the given polygons into triangles and then use the fact that the sum of the angles in each triangle is 180_.

Parts (d) and (e) of this task constitute a very advanced application of the skill of making use of structure: in (d) students are being asked to use the defining property of even and odd functions to manipulate expressions involving function notation. In (e) they are asked to see the structure in the system of two equations involving functions.

This task is not about computing the final price of the shirt but about using the structure in the computation to make a general argument.

This simple conceptual problem does not require algebraic manipulation, but requires students to articulate the reasoning behind each statement.

This task illustrates A-SSE.1a because it requires students to identify expressions as sums or products and interpret each summand or factor.

Although this task is quite straightforward, it has a couple of aspects designed to encourage students to attend to the structure of the equation and the meaning of the variables in it. It fosters flexibility in seeing the same equation in two different ways, and it requires students to attend to the meaning of the variables in the preamble and extract the values from the descriptions.
The course consists of a sampling of topics from algebraic combinatorics. The topics include the matrix-tree theorem and other applications of linear algebra, applications of commutative and exterior algebra to counting faces of simplicial complexes, and applications of algebra to tilings.
The main aims of this seminar will be to go over the classification of surfaces (Enriques-Castelnuovo for characteristic zero, Bombieri-Mumford for characteristic p), while working out plenty of examples, and treating their geometry and arithmetic as far as possible.

Topics vary from year to year. Fall Term: Numerical properties and vanish theorems for ample, nef, and big line bundles and vector bundles; multiplier ideals and their applications
This course provides an introduction to algebraic number theory. Topics covered include dedekind domains, unique factorization of prime ideals, number fields, splitting of primes, class group, lattice methods, finiteness of the class number, Dirichlet's units theorem, local fields, ramification, discriminants.
Content varies from year to year. Introduces new and significant developments in algebraic topology with the focus on homotopy theory and related areas. Spring 2003: An introduction to higher algebraic K-theory.