- Subject:
- Arts and Humanities
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Date Added:
- 01/06/2016

This activity provides instructions for using a flashlight and aquarium (or other container of water) to explain why the sky is blue and sunsets are red. When the white light from the sun shines through the earth's atmosphere, it collides with gas molecules with the blue light scattering more than the other colors, leaving a dominant yellow-orange hue to the transmitted light. The scattered light makes the sky blue; the transmitted light makes the sunset reddish orange. The section entitled What's Going On? explains this phenomena.

"This course examines electric and magnetic quasistatic forms of Maxwell's equations applied to dielectric, conduction, and magnetization boundary value problems. Topics covered include: electromagnetic forces, force densities, and stress tensors, including magnetization and polarization; thermodynamics of electromagnetic fields, equations of motion, and energy conservation; applications to synchronous, induction, and commutator machines; sensors and transducers; microelectromechanical systems; propagation and stability of electromechanical waves; and charge transport phenomena. Acknowledgments The instructor would like to thank Thomas Larsen and Matthew Pegler for transcribing into LaTeX the homework problems, homework solutions, and exam solutions."

Students are introduced to sound energy concepts and how engineers use sound energy. Through hands-on activities and demonstrations, students examine how we know sound exists by listening to and seeing sound waves. They learn to describe sound in terms of its pitch, volume and frequency. They explore how sound waves move through liquids, solids and gases. They also identify the different pitches and frequencies, and create high- and low-pitch sound waves.
Play with a 1D or 2D system of coupled mass-spring oscillators. Vary the number of masses, set the initial conditions, and watch the system evolve. See the spectrum of normal modes for arbitrary motion. See longitudinal or transverse modes in the 1D system.
This course provides an introduction to optical science with elementary engineering applications. Topics covered in geometrical optics include: ray-tracing, aberrations, lens design, apertures and stops, radiometry and photometry. Topics covered in wave optics include: basic electrodynamics, polarization, interference, wave-guiding, Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction, image formation, resolution, space-bandwidth product. Analytical and numerical tools used in optical design are emphasized. Graduate students are required to complete assignments with stronger analytical content, and an advanced design project.
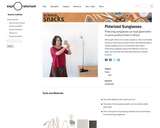
In this activity, learners explore how polarizing sunglasses can help diminish road glare. By rotating a pair of polarizing sunglass lenses or other polarizing materials, learners will discover that some angles are better at reducing glare than others. Learners observe light from the sky, reflected from a mirror, or reflected from the surface of a pond. Use this activity to introduce learners to principles of light and polarization.
The electric field lines from a point charge evolve in time as the charge moves. Watch radiation propagate outward at the speed of light as you wiggle the charge. Stop a moving charge to see bremsstrahlung (braking) radiation. Explore the radiation patterns as the charge moves with sinusoidal, circular, or linear motion. You can move the charge any way you like, as long as you don’t exceed the speed of light.