Learning what polynomials are, how to add, subtract and multiply them.
- Subject:
- Algebra
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
- Provider:
- Michigan Virtual
- Author:
- Alison Chatten
- Date Added:
- 06/30/2017

Learning what polynomials are, how to add, subtract and multiply them.
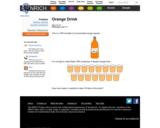
This Nrich question tackles proportion in a real context. It also needs systematic thinking to sort out the information and take a step-by-step route to the solution.
This Nrich activity offers free exploration that can help youngsters with their development of the concepts associated with fractions. It provides a chance for meaningful mathematical discussion and sharing of current understanding, in addition to offering opportunities for challenging misconceptions.
Using Desmos software, students will manipulate equations to fit certain graphs.

This simple conceptual task focuses on what it means for a number to be a solution to an equation, rather than on the process of solving equations.
This Nrich problem is in three parts, with each part becoming more open-ended and requiring more reasoning, giving students a chance to develop their skills at solving problems with fractions and then applying those skills in a more challenging context. By listening to others' approaches, students will be encouraged to persevere and continue to improve on their solution to the final part of the problem.
In this Nrich problem students apply their knowledge of area and percentages to extend their understanding.

This task requires students to answer questions about the structure of an expression.
This Nrich problem is a good challenge for those children who are competent with calculating using fractions and decimals.
In this Nrich problem students extend their understanding of percentages in a multi-step real world situation.

This is a simple exercise in creating equations from a situation with many variables. By giving three different scenarios, the problem requires students to keep going back to the definitions of the variables, thus emphasizing the importance of defining variables when you write an equation. In order to reinforce this aspect of the problem, the variables have not been given names that remind the student of what they stand for. The emphasis here is on setting up equations, not solving them.
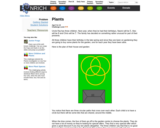
In this Nrich activity, students explore combinations in a situation with constraints. The combinations are complicated by sets and subsets. The situation uses a Venn Diagram.

In this math activity, learners observe and sketch cracking patterns in pavement. Learners use a protractor to measure and label the angles of their sketches and conclude if some angles are more common than others.
Created for book lovers who like data. Whether you are an English teacher, professor, student, or run-of-the-mill bibliophile, Plotting Plots can help you explore ways to use data and technology to deepen the joy of reading.
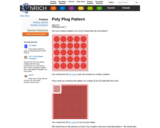
Students create and extrapolate patterns on an array for this Nrich activity.

Students revisit the fundamental theorem of algebra as they explore complex roots of polynomial functions. They use polynomial identities, the binomial theorem, and Pascals Triangle to find roots of polynomials and roots of unity. Students compare and create different representations of functions while studying function composition, graphing functions, and finding inverse functions.
Find the rest of the EngageNY Mathematics resources at https://archive.org/details/engageny-mathematics.

This module revisits trigonometry that was introduced in Geometry and Algebra II, uniting and further expanding the ideas of right triangle trigonometry and the unit circle. New tools are introduced for solving geometric and modeling problems through the power of trigonometry. Students explore sine, cosine, and tangent functions and their periodicity, derive formulas for triangles that are not right, and study the graphs of trigonometric functions and their inverses.

(Nota: Esta es una traducción de un recurso educativo abierto creado por el Departamento de Educación del Estado de Nueva York (NYSED) como parte del proyecto "EngageNY" en 2013. Aunque el recurso real fue traducido por personas, la siguiente descripción se tradujo del inglés original usando Google Translate para ayudar a los usuarios potenciales a decidir si se adapta a sus necesidades y puede contener errores gramaticales o lingüísticos. La descripción original en inglés también se proporciona a continuación.)
Los estudiantes vuelven a visitar el teorema fundamental del álgebra mientras exploran raíces complejas de funciones polinomiales. Utilizan identidades polinomiales, el teorema binomial y el triángulo de Pascal para encontrar raíces de polinomios y raíces de la unidad. Los estudiantes comparan y crean diferentes representaciones de funciones mientras estudian composición de funciones, gráficos de funciones y encuentran funciones inversas.
Encuentre el resto de los recursos matemáticos de Engageny en https://archive.org/details/engageny-mathematics.
English Description:
Students revisit the fundamental theorem of algebra as they explore complex roots of polynomial functions. They use polynomial identities, the binomial theorem, and Pascals Triangle to find roots of polynomials and roots of unity. Students compare and create different representations of functions while studying function composition, graphing functions, and finding inverse functions.
Find the rest of the EngageNY Mathematics resources at https://archive.org/details/engageny-mathematics.

(Nota: Esta es una traducción de un recurso educativo abierto creado por el Departamento de Educación del Estado de Nueva York (NYSED) como parte del proyecto "EngageNY" en 2013. Aunque el recurso real fue traducido por personas, la siguiente descripción se tradujo del inglés original usando Google Translate para ayudar a los usuarios potenciales a decidir si se adapta a sus necesidades y puede contener errores gramaticales o lingüísticos. La descripción original en inglés también se proporciona a continuación.)
Este módulo revisa la trigonometría que se introdujo en la geometría y el álgebra II, uniendo y ampliando aún más las ideas de la trigonometría del triángulo recto y el círculo unitario. Se introducen nuevas herramientas para resolver problemas geométricos y de modelado a través del poder de la trigonometría. Los estudiantes exploran funciones sinuso, coseno y tangentes y su periodicidad, derivan fórmulas para triángulos que no son correctos y estudian los gráficos de las funciones trigonométricas y sus inversos.
English Description:
This module revisits trigonometry that was introduced in Geometry and Algebra II, uniting and further expanding the ideas of right triangle trigonometry and the unit circle. New tools are introduced for solving geometric and modeling problems through the power of trigonometry. Students explore sine, cosine, and tangent functions and their periodicity, derive formulas for triangles that are not right, and study the graphs of trigonometric functions and their inverses.

This task compares the usefulness of different forms of a quadratic expression. Students have to choose which form most easily provides information about the maximum value, the zeros and the vertical intercept of a quadratic expression in the context of a real world situation. Rather than just manipulating one form into the other, students can make sense out of the structure of the expressions.