War on Drugs Slideshow
- Subject:
- Career and Technical Education
- Criminal Justice
- Material Type:
- Interactive
- Provider:
- Michigan Virtual
- Date Added:
- 07/29/2019

War on Drugs Slideshow
Peacemaking Criminology Slideshow
This collection uses primary sources to explore AIDS activism during the 1980s. Digital Public Library of America Primary Source Sets are designed to help students develop their critical thinking skills and draw diverse material from libraries, archives, and museums across the United States. Each set includes an overview, ten to fifteen primary sources, links to related resources, and a teaching guide. These sets were created and reviewed by the teachers on the DPLA's Education Advisory Committee.
What does “civil rights” mean in the Trump era? How and why is the category evolving? This Teach-Out focuses on the civil rights aspects of two current debates–health care and the President’s seven-country travel ban–looking at politics, protest, and law. To understand these better, you will learn about foundational civil rights history dating back to Reconstruction (after the Civil War). You will also hear the perspectives of scholars in law, sociology, and political science, as well as civil rights advocates, who will all discuss how civil rights are defended and contested, often growing and contracting in response to other demands and debates. This Teach-Out ends with a call to action for you: How will you participate as our nation defines our rights?
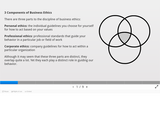
Personal vs. Business Ethics

Give Civics, Law, U.S. History students practice in analyzing historical Primary Source document and connect to contemporary news. Develop writing process to incorporate claims, evidence, and reasoning.
This learning object will give your students an opportunity to think critically about the bill of rights in real life situations and leverage technology in such a way that they can learn in a fun and engaging way. The students will begin by studying the Bill of Rights at the link below, then the class will play the Kahoot Quiz online using any digital device with an internet connection. The quiz will require the students to read a real life situation and choose which of the ten amendments of the Bill of Rights is associated with that right. Critical thinking and application of skills will be required to win the game. Students could then be asked to join Kahoot and create their own Bill of Rights quiz game.
Interdisciplinary survey of people of African descent that draws on the overlapping approaches of history, literature, anthropology, legal studies, media studies, performance, linguistics, and creative writing. This course connects the experiences of African-Americans and of other American minorities, focusing on social, political, and cultural histories, and on linguistic patterns.
This learning object will have your students understand how important protecting ourselves from government is and how necessary a bill or rights is.
Your students will share a google doc with their group for collaboration on a bill of classroom rights and then come together as a class to choose the top ten rights by having the students vote using surveymonkey.com to allow students to vote via a chromebook or computer. When finished have a class representative present your list of rights to the principal for ratification.

After completing the lessons in this unit, students will be able to summarize the contents of the First Amendment and give examples of speech that is protected by the Constitution and speech that is not protected by the Constitution.
This unit asks students to consider the permissible restrictions schools can place on students’ freedom of speech, as they learn about the (fictional, but realistic) case of Davis v. Ann Arbor School Board. Students will either conduct a mock negotiation in which they will try to resolve a First Amendment-related conflict between a student and his public high school, or a mock argument in which they will argue for one side in front of a panel of student judges.
This Unit contains 9 lessons:
Lesson 1: Are schools permitted to limit students’ First Amendment freedom of speech?
Lesson 2: Under what circumstances may a school punish student speech?
Lesson 3: How does the law apply to our case?
Lesson 4: What are the key elements of negotiation?
Lesson 5: How can parties use negotiation to achieve the best solution?
Lesson 6: Is negotiation an effective tool in the legal process?
Lesson 7: What is a mock argument?
Lesson 8: How do I prepare for a mock argument?
Lesson 9: How do attorneys conduct oral arguments to advocate for their clients?

In all civilized nations, attempts are made to define and buttress human rights. The core of the concept is the same everywhere: Human rights are the rights that one has simply because one is human. They are universal and equal. The following pubilcation gives an overview of Human Rights across the globe.
In all civilized nations, attempts are made to define and buttress human rights. The core of the concept is the same everywhere: Human rights are the rights that one has simply because one is human. They are universal and equal. The following pubilcation gives an overview of Human Rights across the globe.

What arguments were put forth in objection to the Sedition Act? Supporters of Thomas Jefferson and James Madison believed the Sedition Act was designed to repress political opposition to President John Adams and the Federalists.
This lesson helps students learn about the judicial system through simulating a real court case involving student free speech rights. In addition to learning about how the Supreme Court operates, students will explore how the Supreme Court protects their rights, interprets the Constitution, and works with the other two branches of government.
This unit introduces students to the concept of civil rights litigation. It asks students to consider how the litigation process reflects the fundamental values and principles of American constitutional government. By the end of this unit, students should be prepared to talk about how the civil litigation process reflects these values and principles and to describe civil rights litigation and its current scope.
Lesson 1: What is Litigation?
Lesson 2: What are the Steps of Litigation?
Lesson 3: What is Civil Rights Litigation?

In this unit, students will participate in a mock trial that explores the rights and restrictions on individuals attempting to practice their own religion. Students will first familiarize themselves with the Religious Freedom and Restoration Act (“RFRA”), which was intended to further protect First Amendment rights. Students will then read and analyze case documents adapted from a real federal court case, Singh v. Carter, which involved a conflict between a soldier’s desire to exercise his religious practices and the U.S. Army’s interest in protecting its soldiers through uniform and safety requirements.
After learning about the relevant law and facts, students will participate in a mock trial that will allow them to use their knowledge to persuade judges to find either that the soldier’s religious practice is protected by RFRA, or that the Army has an overriding safety concern that forbids the soldier from exercising his religion. The mock trial allows students to assume roles as members of the plaintiff’s team, members of the defendant’s team, neutral judges, or impartial courtroom participants. This allows every student to have a substantive role in deciding or observing a dispute that remains pertinent today. Students engage in the authentic tasks of examining and weighing evidence, and using facts and evidence to formulate and present claims.
This Unit contains 7 lessons:
Lesson 1: Religious Freedom Mock Trial
Lesson 2: Articulating and Applying the Law
Lesson 3: Understanding the Evidence
Lesson 4: Developing a Theory of the Case
Lesson 5: Preparing for Trial
Lesson 6: The Trial
Lesson 7: Debrief and Reflection